Data Acquisition
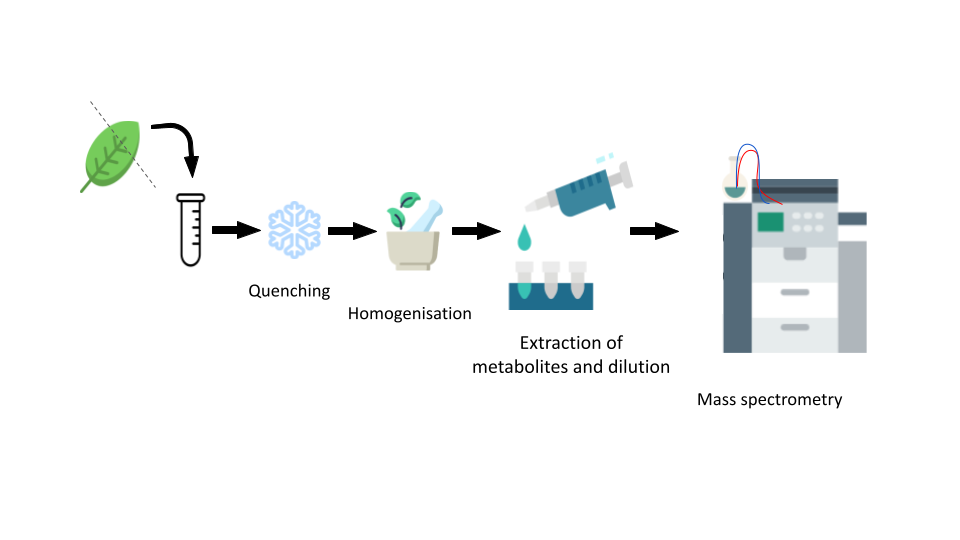
There are many options for metabolomics data acquisition. To some extent your choices will be limited by what resources you have available (cost, time, equipment available in labs you have access to, expertise of technicians in the facility you use).
In this guide we focus on processing data from three data acquistion approaches: MALDI, DI-ESI-MS and LC-ESI-MS because these are the three we commonly use in our facility and want to support users to process their data. GC-MS is also often used for untargeted metabolomics and workflows for data processing are available ***
| MALDI | DI-ESI-MS | LC-ESI-MS | GC-ESI-MS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fast | Fast | ||
| Minimal fragmentation | |||
| Good for non-polar metabolites | Good for low m/z compounds | Better coverage of secondary metabolites | Targets non-polar and volatile metabolites |
| Non-targeted analysis | Non-targeted analysis | More targeted analysis | More targeted analysis |
| Higher quality annotation | NIST library matching for ease of identification |
📖 For an overview and guidance on choosing an MS approach, please refer to: Katam, R.; Lin, C.; Grant, K.; Katam, C.S.; Chen, S. Advances in Plant Metabolomics and Its Applications in Stress and Single-Cell Biology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6985. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23136985
The data acquisition methods used will define how the data is processed, so in this workflow we have included an interactive workflow diagram to help you navigate the steps required depending on the MS approach used.